
In the ever-evolving world of logistics, AI in Logistics is a game-changer, transforming how goods are produced, stored, and delivered. From predictive analytics to autonomous vehicles, AI’s integration into logistics is revolutionizing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer experience. This article explores the pivotal role AI is playing in reshaping logistics operations, enabling smarter and more agile supply chains.
With growing demand for faster delivery times, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences, logistics companies are turning to advanced technologies to transform their operations. AI and ML are at the forefront of logistics transformation. These technologies analyze massive amounts of data to improve decision-making processes. AI is used in various logistics applications, including route optimization, demand forecasting, and autonomous vehicles. With machine learning, logistics companies can adapt to changing conditions in real time, improving efficiency and reducing costs.

- AI-Driven Route Planning: Optimizing Logistics for Efficiency
- AI-Powered Autonomous Vehicles and Drones in Logistics
- AI Predictive Analytics in Logistics: Accurate Demand Forecasting
- Enhancing Warehouse Management with AI-Driven Automation
- Predictive Maintenance in Logistics: Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
- Improving Customer Experience with AI in Logistics
- AI for Risk Management and Fraud Detection in Logistics
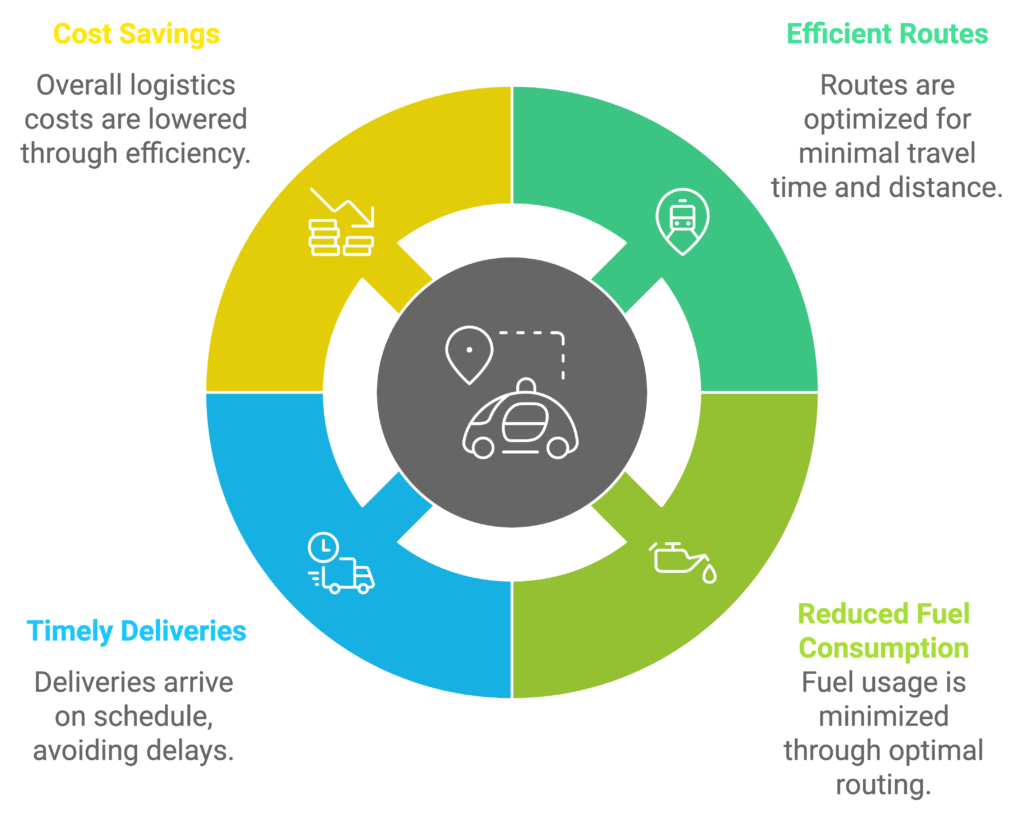
AI-Driven Route Planning: Optimizing Logistics for Efficiency
One of the most significant contributions of AI in logistics is the optimization of route planning. Traditionally, route planning relied on manual calculations or static algorithms that failed to adapt to dynamic real-world conditions. AI algorithms, powered by machine learning (ML), can analyze vast amounts of data such as traffic patterns, weather conditions, and road hazards in real time. These insights enable logistics companies to plan the most efficient routes, reducing fuel consumption, delivery times, and costs.
For instance, AI-driven platforms can provide real-time recommendations for alternate routes when accidents or traffic congestion occur. This reduces fuel costs and ensures timely deliveries.

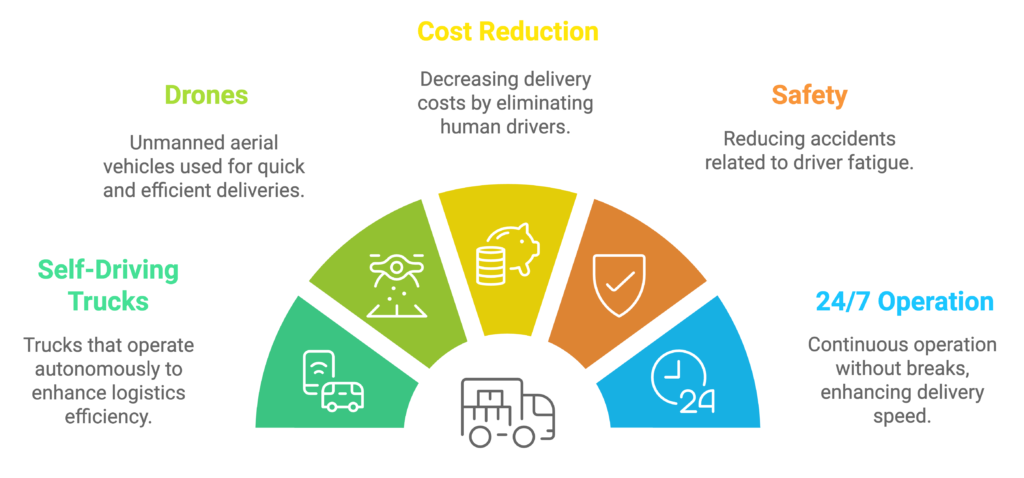
AI-Powered Autonomous Vehicles and Drones in Logistics
AI is at the core of the development of autonomous delivery systems, including self-driving trucks and drones. These technologies promise to revolutionize logistics by making deliveries faster and more cost-effective, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
Autonomous vehicles can operate 24/7, without the need for human drivers, significantly reducing labor costs and mitigating the risk of driver fatigue-related accidents. Similarly, drones are being tested for last-mile delivery, particularly in rural or congested urban areas where conventional delivery methods may be inefficient.
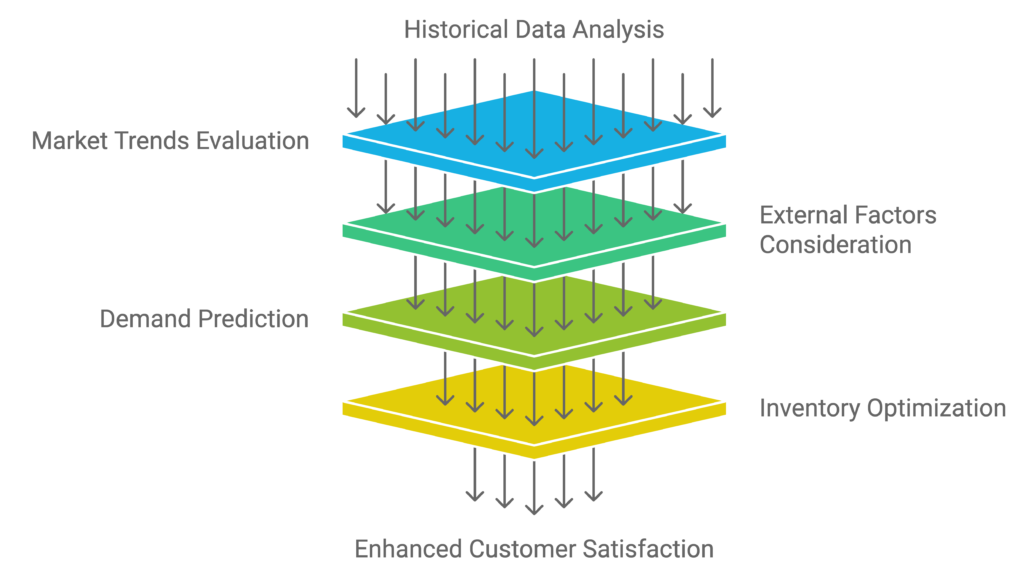
AI Predictive Analytics in Logistics: Accurate Demand Forecasting
One of the key challenges in logistics is managing fluctuating demand. AI helps solve this by providing accurate demand forecasting through predictive analytics. AI systems analyze historical data, market trends, and external factors like seasonal variations to predict future demand with high precision.
This forecasting capability allows companies to optimize inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. As a result, businesses can ensure that the right products are available at the right time, improving customer satisfaction while minimizing warehousing costs.

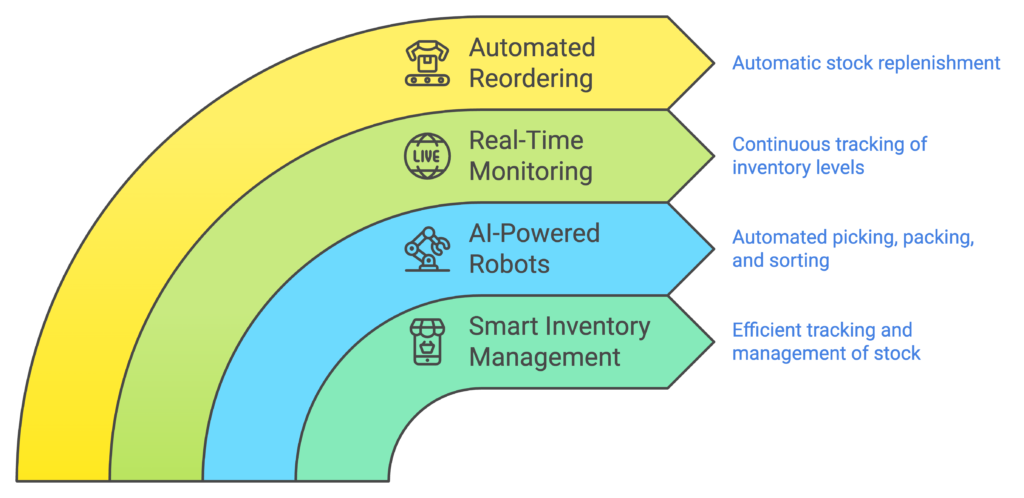
Enhancing Warehouse Management with AI-Driven Automation
AI-driven automation is streamlining warehouse operations by enabling smart inventory management. Robots and automated systems powered by AI are being used to perform tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting goods with speed and precision. These systems are capable of working around the clock, thus increasing productivity and reducing the chances of human error.
Additionally, AI-enabled sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices allow for real-time monitoring of inventory levels. This means that logistics companies can automatically reorder supplies when stock levels drop below a certain threshold, ensuring seamless operations and reducing the cost of manual inventory checks.
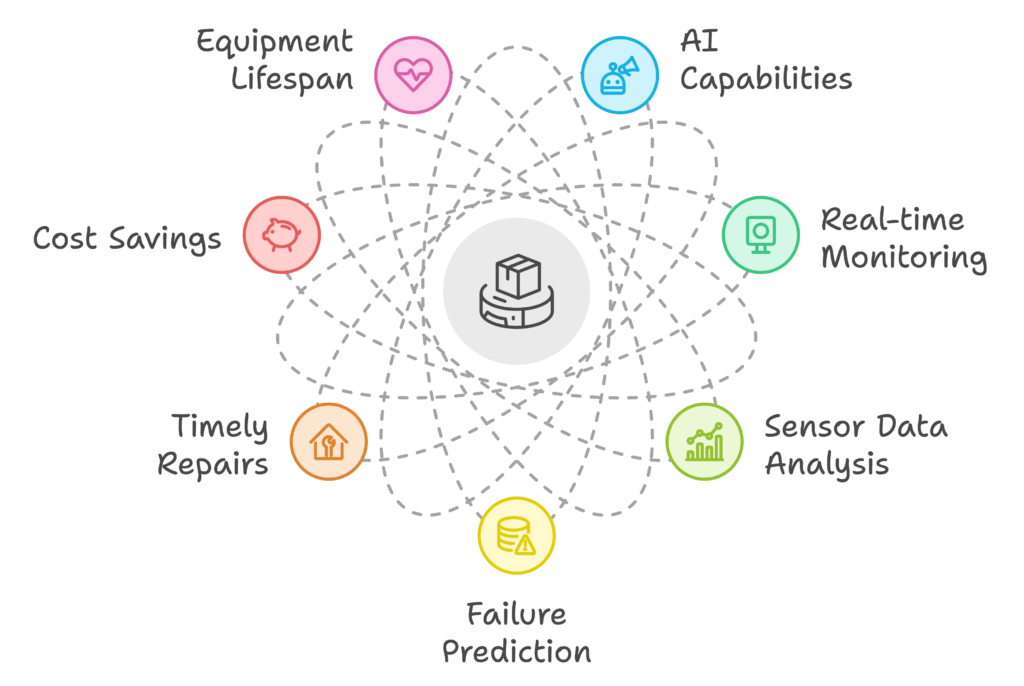
Predictive Maintenance in Logistics: Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
AI’s predictive capabilities extend beyond forecasting demand; it is also being used to maintain the health of logistics infrastructure. Predictive maintenance systems use AI to monitor the condition of trucks, forklifts, and other machinery in real time. By analyzing data from sensors embedded in these machines, AI can predict potential failures before they happen, allowing for timely repairs and reducing costly downtime.
This approach not only saves money but also extends the lifespan of equipment, ensuring that logistics operations continue to run smoothly and efficiently.

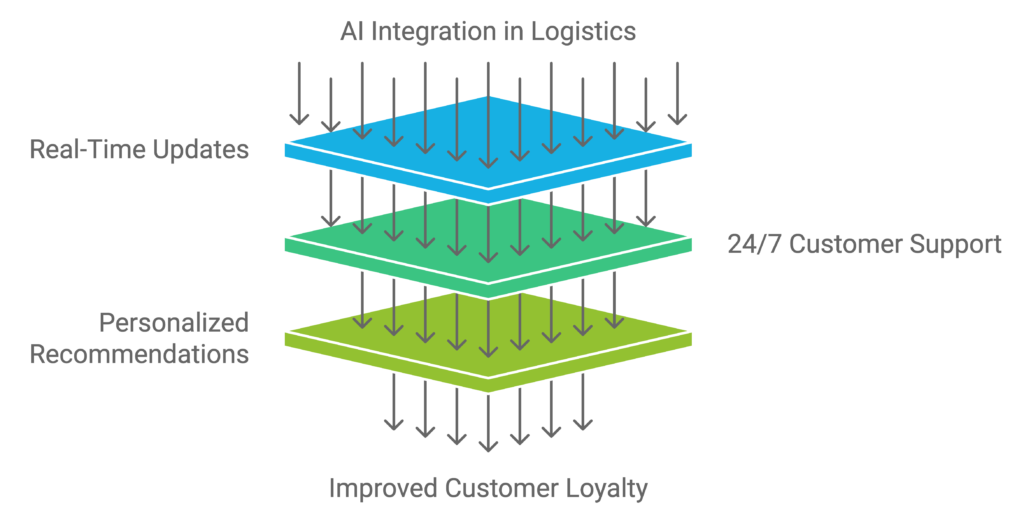
Improving Customer Experience with AI in Logistics
AI is enhancing the customer experience by providing real-time updates on shipment status, delivery times, and potential delays. Chatbots and AI-driven customer service platforms are available 24/7 to answer inquiries, assist with order tracking, and even handle complaints. This level of automation improves communication and transparency, ensuring that customers remain informed and satisfied.
Moreover, AI can personalize the customer experience by offering tailored recommendations based on their previous purchases or preferences, thus driving customer loyalty.
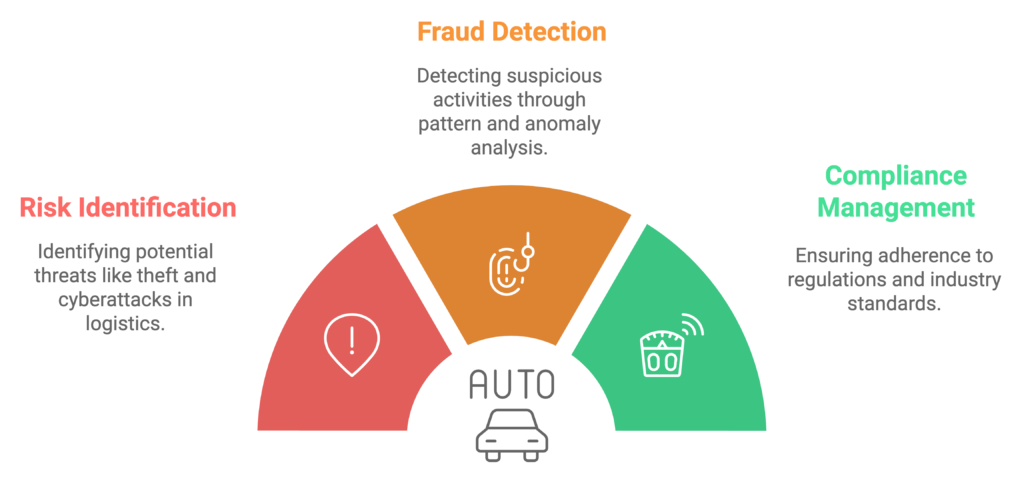
AI for Risk Management and Fraud Detection in Logistics
AI plays a critical role in risk management by identifying potential threats to the supply chain, such as theft, fraud, or cyberattacks. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in transactional data, AI systems can detect suspicious activities and alert logistics companies to take preventive action.
Furthermore, AI helps in compliance management by ensuring that logistics companies adhere to regulations and industry standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties.

Virtust Technologies can leverage AI to solve various challenges for startups and enterprises by implementing the following use cases: